Shedding fats relies on making a caloric deficit, which implies nailing at the least one (and ideally each) of two situations: consuming fewer energy than wanted to keep up your present weight and burning extra energy than you devour.
That final half may be tough. Determining the variety of energy burned by way of train isn’t any small job, as there are various components that impression that complete (e.g., weight, intercourse, age, genes, train depth). What’s extra, analysis suggests we could overestimate what number of energy we burn in a single exercise by as a lot as 4 occasions the precise quantity!
However relaxation assured, it may be executed. Right here, we assist minimize by way of the confusion. Take into account this your primer on energy burned throughout train.
2 Greatest Elements in Energy Burned: Length and Depth

On the subject of caloric burn from train, length and depth are the 2 key components that decide your remaining tally.
“Of the 2, depth is an important, as a result of it influences how lengthy your metabolism stays elevated when you cease figuring out,” says Trevor Thieme, C.S.C.S.
You may burn extra energy throughout an hour-long, steady-state cardio session than throughout a fast high-intensity interval coaching (HIIT) session. However that HIIT exercise will hold your metabolism elevated lengthy after you’re executed exercising as your physique recovers.
This “afterburn” impact is named extra post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). The longer and extra intense your exercise is, the longer and extra intense your restoration will probably be — and the extra fats you’ll in the end burn. Why? As a result of fats is what your physique makes use of to gas your restoration.
Calculating the precise variety of energy burned through EPOC may be tough, however in accordance with a research printed within the Worldwide Journal of Sport Diet and Train Metabolism, contributors who spent simply two minutes sprint-cycling burned sufficient energy within the 24 hours afterward to equal half an hour of steady-state biking.
Does weight have an effect on what number of energy you burn?
As a basic rule, the extra you weigh, the extra energy you’ll burn throughout train — or some other time. “That’s merely a operate of the power required to maneuver your physique,” says Thieme.
That mentioned, your muscle-to-fat ratio may also decide what number of energy you’ll burn each day: “A lean, muscular 180-pound man will burn extra energy than an chubby 180-pound man throughout the identical exercise just because the muscular man has extra ‘metabolically lively’ tissue,” Thieme says.
Does top have an effect on what number of energy you burn?
Peak can have an effect on the variety of energy burned by way of train, however solely as a result of top influences weight.
“When you’re tall, you’re possible going to weigh extra [than someone who’s shorter],” says Tim Church, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., chief medical officer at Wondr Well being. Nonetheless, in the event you weigh lower than somebody who’s shorter than you, your caloric burn could find yourself being decrease.
How Do You Calculate Energy Burned?

To determine what number of energy you burn from train, look to a technique generally utilized by train scientists to estimate power expenditure: metabolic equivalents.
What’s a metabolic equal (MET)?
A metabolic equal, or MET, is a measure of the quantity of oxygen you devour throughout bodily exercise, expressed in energy. METs are calculated by multiplying 3.5 milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of physique weight by the variety of minutes of exercise. To make use of a real-life instance, a 70-kg (154-lb.) individual will burn roughly 1.5 energy per minute whereas sitting in a chair.
What are energy?
We all know energy are central to weight misplaced and gained, however few of us can clarify what a calorie is.
A calorie — or Calorie, with a capital “C” — is mostly a kilocalorie, which implies it’s composed of 1,000 energy. One Calorie can warmth 1 kilogram of water by 1 diploma Celsius.
Your physique makes use of the vitamins (e.g., macronutrients, micronutrients, and phytonutrients) within the Energy you devour to gas bodily exercise, digest meals, hold your mind sharp, and rather more.
The truth is, roughly 60 to 75 % of the energy you want per day get used as much as hold your physique performing at relaxation. This is named your basal metabolic fee (BMR), and it varies from one individual to a different. Key components that decide BMR embody age, physique mass, intercourse, genetics, and organ weight. There are a number of on-line calculators that can provide you an estimated BMR.
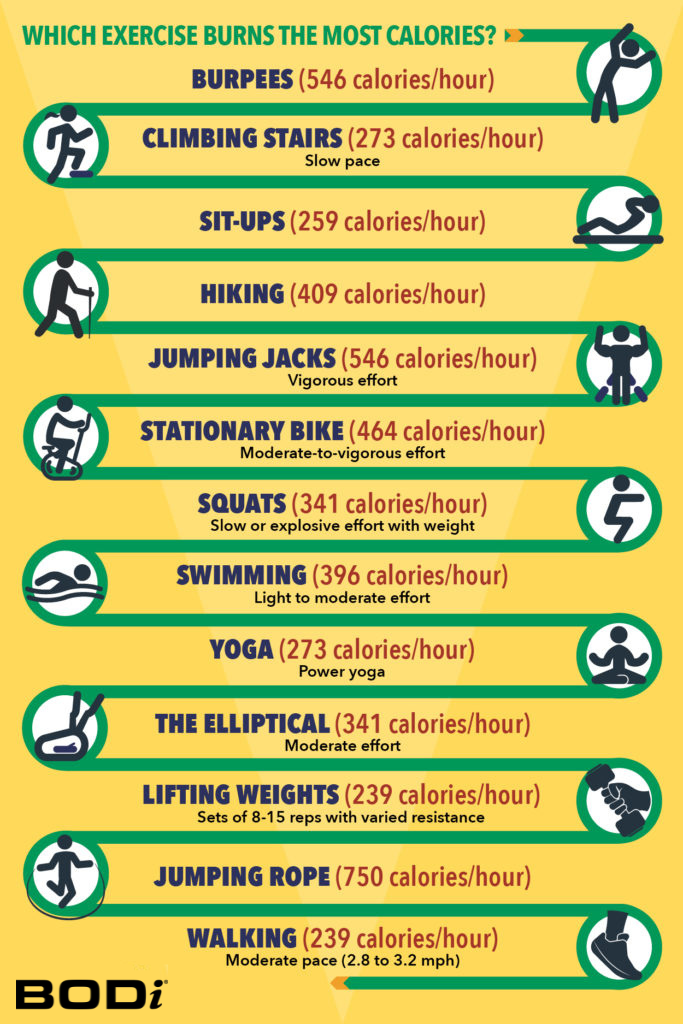
Energy Burned Throughout Totally different Forms of Train
Fortunately, you don’t must be a scientist or mathematician to determine the variety of energy burned throughout your exercise.
The Compendium of Bodily Actions supplies MET values for a variety of actions, whereas Cornell College provides an on-line calculator the place you’ll be able to enter your weight, MET worth to your exercise (from the Compendium), and time to simply calculate the variety of energy you’ll be able to count on to burn.
We’ve used each sources to supply you estimates for the variety of energy a 150-pound individual can burn performing quite a lot of bodily actions.
1. Strolling (239 energy/hour)

Stroll at a average tempo (2.8 to three.2 mph) on a degree floor and also you’ll rack up at the least 3.5 METs. Decide up the tempo to a brisk 3.5 mph, nevertheless, and also you’ll nab 4.3 METs, which works out to 293 energy/hour.
2. Leaping rope (750 energy/hour)
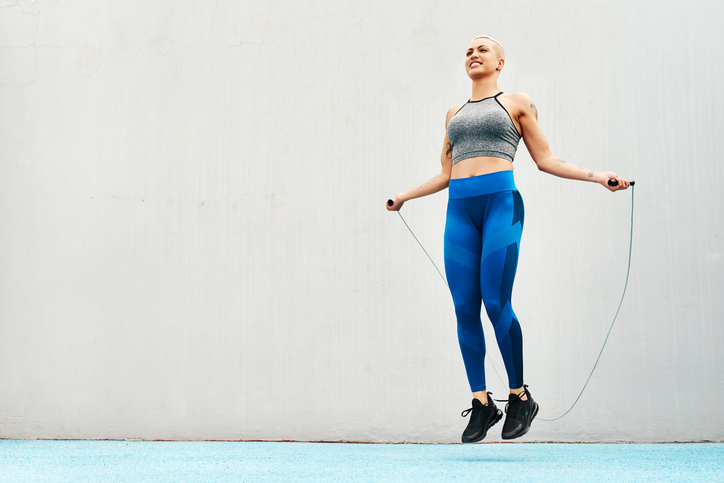

At 11.0 METs, leaping rope is akin to working at a tempo of seven mph (that’s 8.5 minutes per mile). Plus, leaping actions have been proven to promote stronger bones.
3. Lifting weights (239 energy/hour)
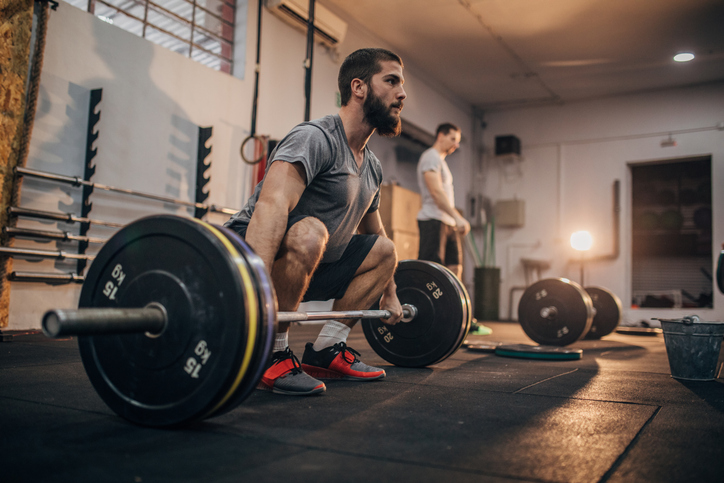

Construct muscle mass and strengthen your bones with some good old school resistance coaching and also you’ll rack up 3.5 METs. And as you’ve already realized, including muscle to your body means you’ll burn extra energy each day.
4. Elliptical (341 energy/hour)

Hop on the joint-friendly elliptical and pedal away at a average effort to get 5.0 METs.
5. Yoga (273 energy/hour)
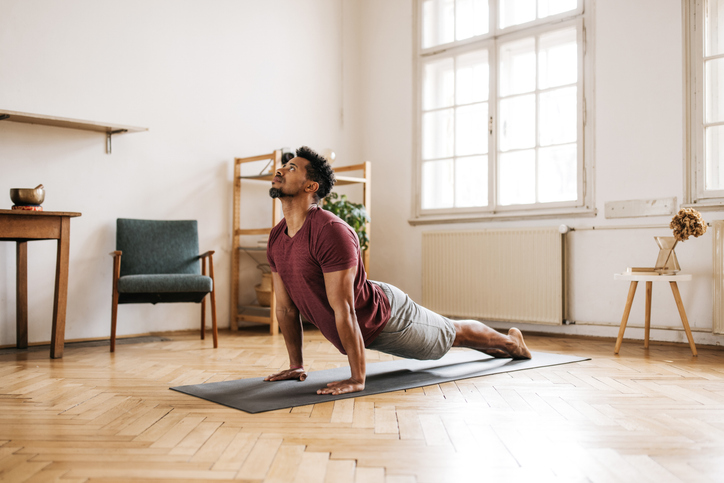

There are a number of yoga types, and every provides its personal degree of depth. Energy yoga, one of many extra intense variations of this historic type of meditation, will provide you with 4.0 METs. Hatha yoga, which is usually slower and gentler, provides solely 2.5 METs (171 energy/hour).
6. Swimming (396 energy/hour)
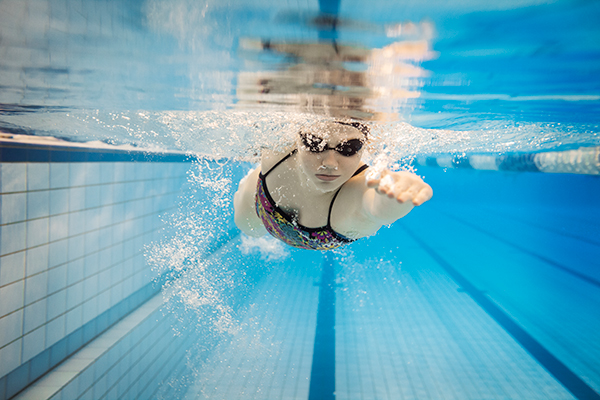

Swimming laps at a light-weight or average effort will provide you with a low-impact exercise that gives 5.8 METs. Bump up the depth to a vigorous effort, nevertheless, and also you’ll get 9.8 METs (668 energy/hour).
7. Squats (341 energy/hour)
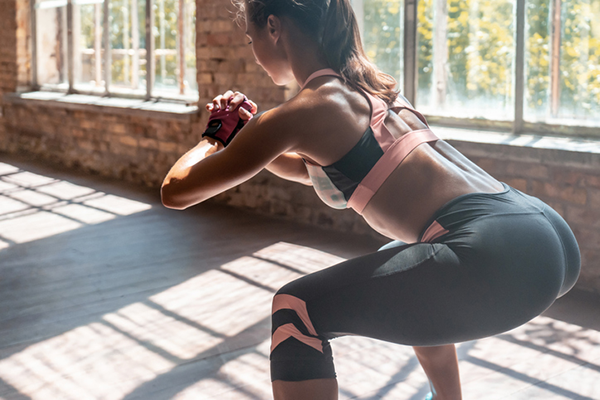

The squat is a multi-joint train that recruits a number of massive muscle teams, together with the glutes and quadriceps. Do them and also you’ll reap 5.0 METs.
8. Stationary bike (464 energy/hour)
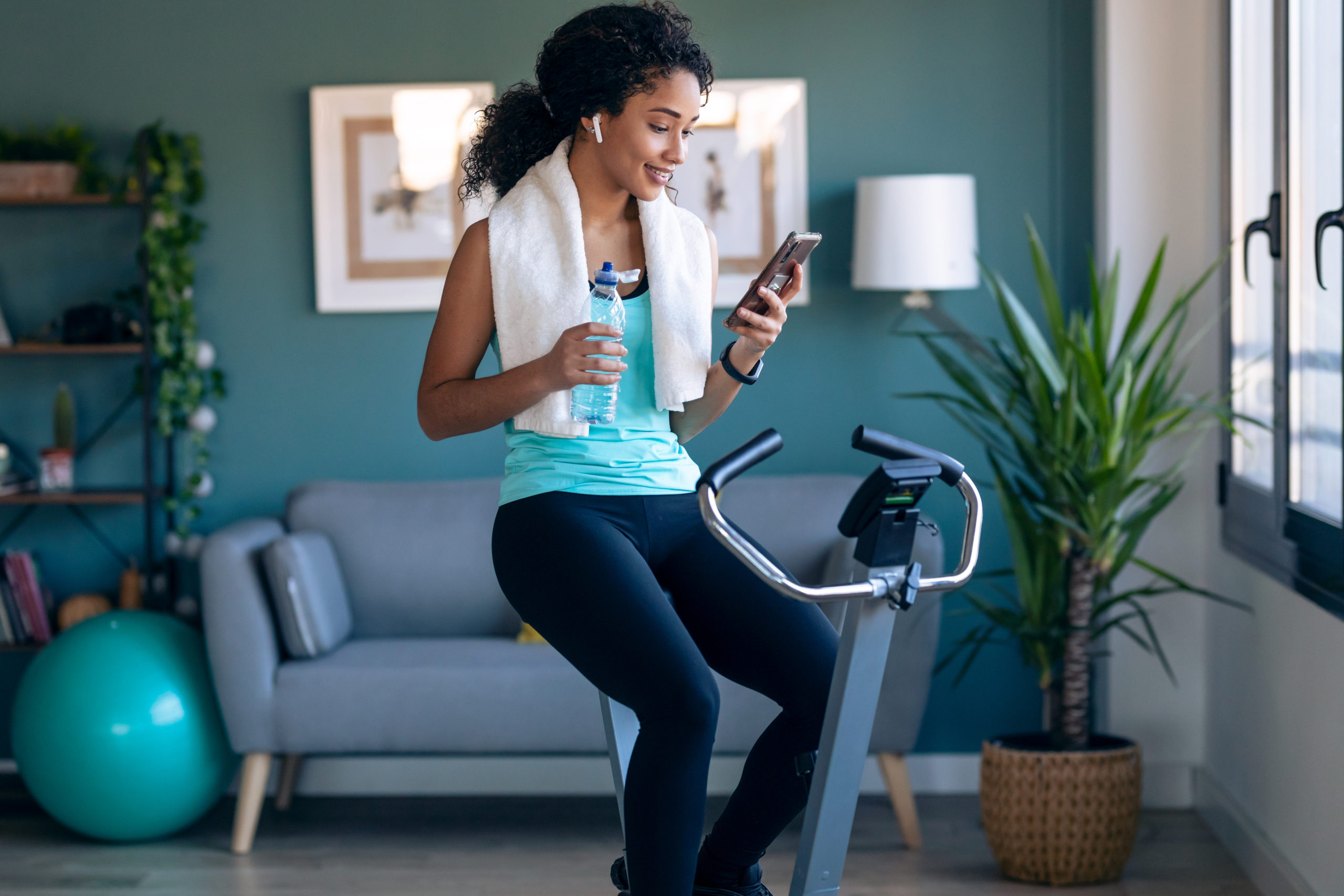

Biking at moderate-to-vigorous effort will not be solely simpler in your joints than different types of cardio train (particularly, working), but it surely’ll additionally web you 6.8 METs.
9.Leaping jacks (546 energy/hour)
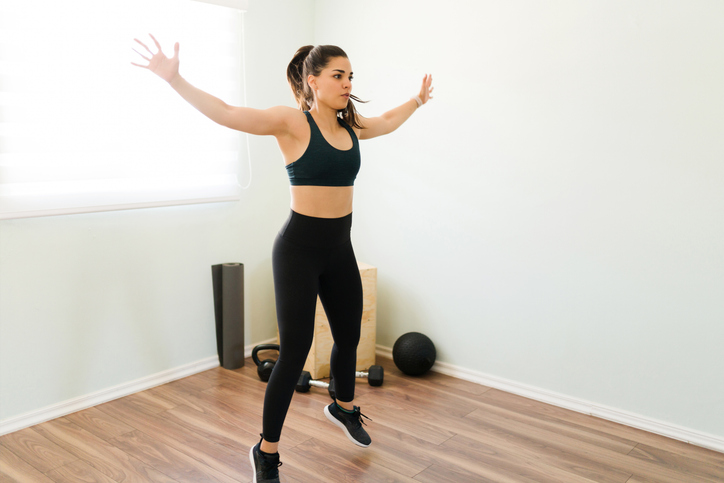

Leaping jacks are thought-about a vigorous type of calisthenics, which is a class of train that entails body weight actions. They’re additionally price 8.0 METs.
10. Mountaineering (409 energy/hour)
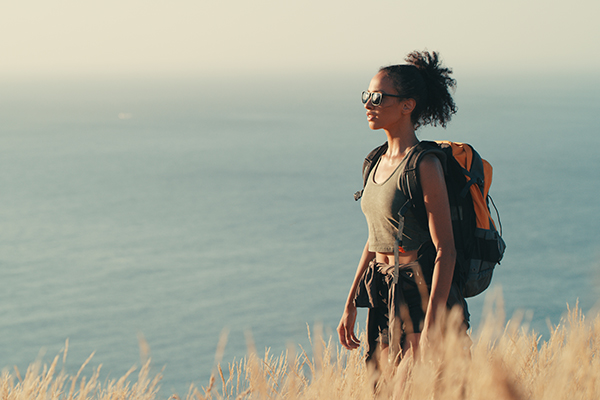

Spending day out in nature will web you roughly 6.0 METs, which is able to solely enhance in the event you add weight (like a vest) or climb hilly terrain.
11. Sit-ups (259 energy/hour)
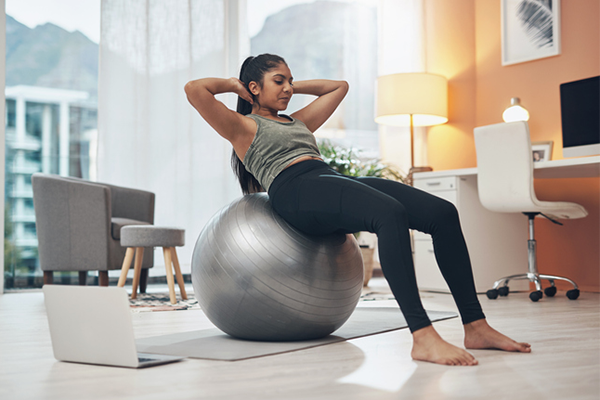

Average-effort calisthenics like old-school sit-ups clock in at 3.8 METs.
12. Climbing stairs (273 energy/hour)
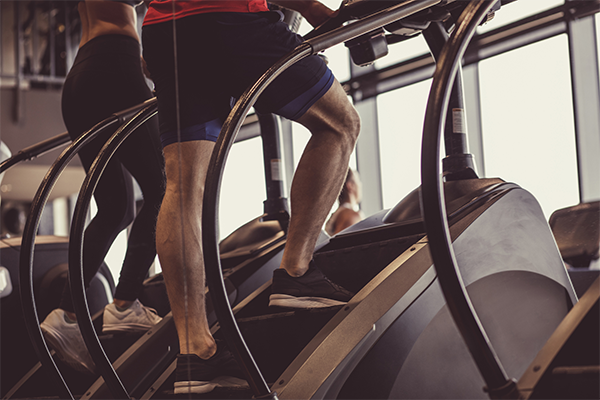

Whether or not you’re on a StairMaster or climbing the steps at work, you’ll rating 4.0 METs in the event you climb at a sluggish, straightforward tempo. However in the event you decide it as much as a quick tempo, you’ll get 8.8 METs (600 energy/hour).
13. Burpees (546 energy/hour)
At 8.0 METs, burpees are a full-body, high-intensity calisthenic train. The truth is, a 2014 research discovered that performing burpees provides cardiovascular advantages just like doing dash intervals on a motorbike.